Cleanup of Windows
Posted in Windows on October 19, 2017 by Adrian Wyssmann ‐ 3 min read
I recently run into the problem that my Harddisk (250GB) run full. Especially when installing Visual Studio, different SDKs (.Net, Android, ...), Microsoft Office, etc. your disk space may become rare. The problem is not only because of the size of these software but also cause Windows is keeping a lot of (unnecessary) files in various locations.
Problem
Beside the obvious things like the trash, which you should empty regularly, there are some stuff which you can do in addition to free up some more space. If you use a tool like TreeSize or WinDirStat to examine the folders, you might come up with some candidates, here some examples
C:\hiberfil.sysC:\Windows\Installer (18GB)C:\Windows\System32\DriverStore (1.7GB)C:\Windows\winsxs (12.4GB)C:\Windows\ccmcache (11.0GB)C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Search (7GB)C:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet FilesC:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\OneNoteC:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Local\TempC:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Local\CrashDumps
First steps
As already mentioned first step of a cleanup of unnecessary occupied space is the cleanup of the Trash. But there is more you can cleanup by running the Disk-Cleanup tool. Just right-click in the Explorer on your C-Drive and click “Properties”. In the Properties dialog you will find a “Disk Cleanup” button which will open another dialog to cleanup different aspects of the system
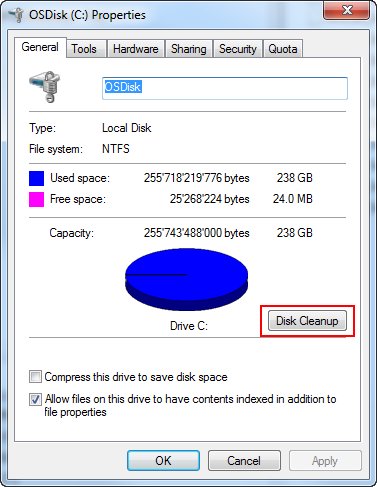
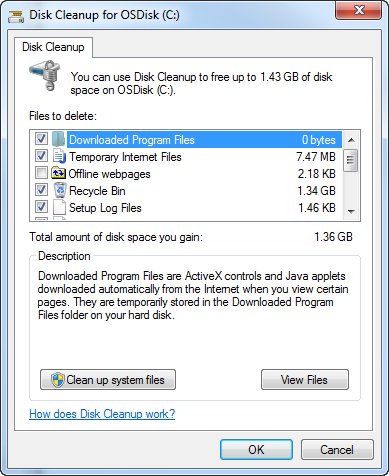
This may already cleanup some space but might not be enough. So let’s examine the other locations we discovered above.
Hibernation File
Location: C:\hiberfil.sys
If you have Hibernation enabled, this obviously needs space on your disk to save your memory state to disk. The more memory you have the more memory it consumes. Do you really need Hibernation? if not, just disable it and you will get some extra GB free on your disk. Just checkout this page which explains what to do:
- Open a command prompt running as Administrator
- Execute
powercfg.exe /hibernate
Windows Installer Cache
Location: _%WINDIR%_\Installer
Internet is full of the same question: “Why Windows Installer Cache use so much space?” and “How can I clean it up?”. This page gives you a pretty nice overview about Windows Installer and it’s related directories. Summa summarum, installer packages are cached in order to enable maintenance of installations like repairs or installing additional patches. Generally it also says “Do not delete this folder”. However, your friends in Superuser.com came up with ideas how to free up space on your system disk in case you have an additional disk available: https://superuser.com/questions/707767/how-can-i-free-up-drive-space-from-the-windows-installer-folder-without-killing
Ensure no no installations are running on your machine
Make a backup copy of
C:\Windows\InstallerIn Windows Explorer
copy C:\Windows\Installerto another disk, e.g.,D:\C_DRIVE\Windows\InstallerNote: Windows\Installer is a systeIE_delete_temporary_filesm folder and thus invisible so disable option “Hide protected operating system files (Recommended)” in Windows Explorer
Make a Symbolic link to the new Installer location by executing the following commands in a cmd.exe window running as Administrator:
rmdir /s /q C:\Windows\Installer mklink /D C:\Windows\Installer D:\C_DRIVE\Windows\Installer
Remark: I do not recommend to do this step as it may cause other issues like unable to de-install software or even errors when trying to install new software. Concretely when trying to install MSI packages the I got an error 1632
Error 2755. Server returned unexpected error 1632 attempting to install packageDriverStore
Location: C:\Windows\System32\DriverStore
The official documentation describes the driver store in more details:
…driver store is a trusted collection of inbox and third-party driver packages
Component Store
Location: C:\Windows\winsxs
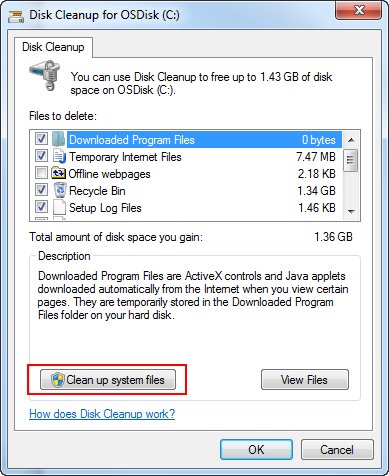
The official documentation describes the component store in more details:
The WinSxS folder is located in the Windows folder, for example c:\Windows\WinSxS. It’s the location for Windows Component Store files. The Windows Component Store is used to support the functions needed for the customization and updating of Windows.
Importantly to understand is also this
The short answer is that the WinSxS folder isn’t as large as it may appear at first glance because size calculations can include Windows binaries located elsewhere which makes the WinSxS folder seem larger than it really is.
Depending on the Windows version there might be ways to cleanup - windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 automatically reduce the size of the WinSxS folder. Checkout Microsoft’s Documentation and follow the steps which fit for your operating system. In addition you always may run the “Clean System Files” with the Disk Cleanup tool described above.
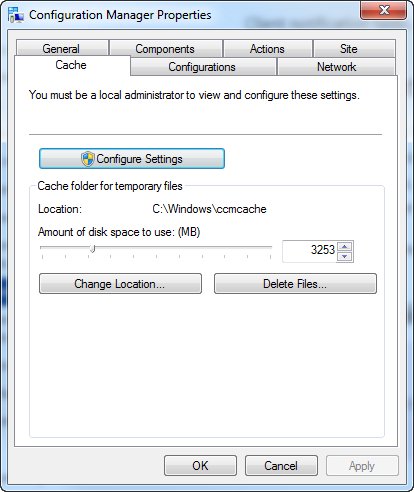
Configuration Manager Cache (ccmcache)
Location: C:\Windows\ccmcache
The
Configuration Manager is something not all of you may have installed but the ones working still with SCVMM might have. The Configuration Manager caches some data locally in the default location %_windir_%\ccmcache. According to
this documentation the default disk space is 5120 MB but in my case is not set. Therefore it is at leas worth to check the properties and limit the cache. In addition the cache location might also be changed. Just open the “Configuration Manager” in the “Control Panel” and then select the “Cache” tab.
Windows Search
Location: C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Search
Windows Search is the desktop search platform which enables instant search of files. The Windows Search Serice (WSS) indexes data - extracts useful information, and then organizes the extracted information so that properties of those documents can be efficiently returned in response to queries - which means the information (index) is stored in a database (Windows.edb). You may find more details in Microsoft’s Documentation about the Indexing process.
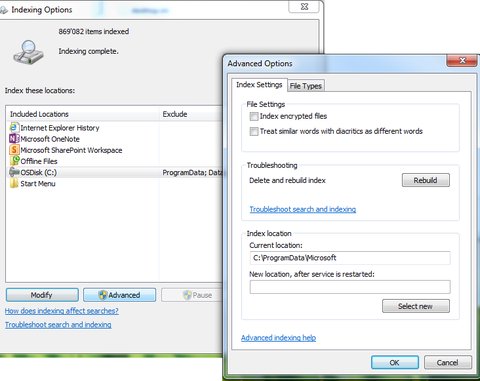
When opening the “Indexing Options” you can control what is and will be indexed. It may be good to revise the “included location” and ensure only necessary stuff is indexed (depends also on your preferences). It’s recommended to start rebuilding the index once you removed or modified some of the locations. You can trigger the rebuild of the index also via Administrative Command prompt as suggested in this post:
net stop "Windows Search"
del %PROGRAMDATA%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.edb
net start "Windows Search"In addition you may change the index location to another place than your system disk (in case you have a second disk available).
Temporary Internet Files (and others)
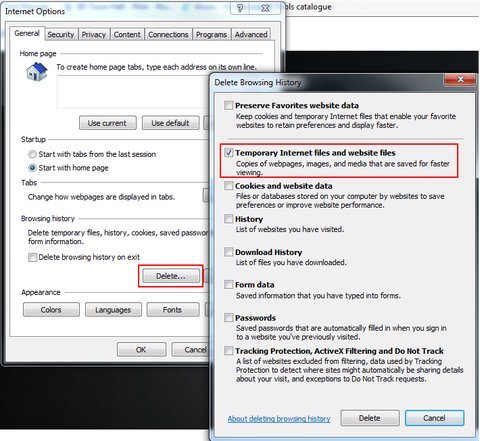
Location: C:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files
Temporary Internet Files can consume a lot of space. The above mentioned location refers to the one form Internet explorer and can be cleaned via the “Internet Options”. Similar apply as well for other browsers where cached internet sites consume space.
More
Sure, there is always more but I think with the topics mentioned above you can already free up some impressive space. Obviously also de-installing unneeded software will free up space which could be otherwise used better.