Manage Terraform with Atlantis in a restricted environment
Posted on July 18, 2022 by Adrian Wyssmann ‐ 8 min read
While we started to use Terraform to manage our Rancher clusters, we started to manually run the terraform commands. This is not the way to go, so we started to look into solutions, starting with Atlantis.
What is Atlantis
atlantis looks quite promising:
Atlantis is an application for automating Terraform via pull requests. It is deployed as a standalone application into your infrastructure. No third-party has access to your credentials.
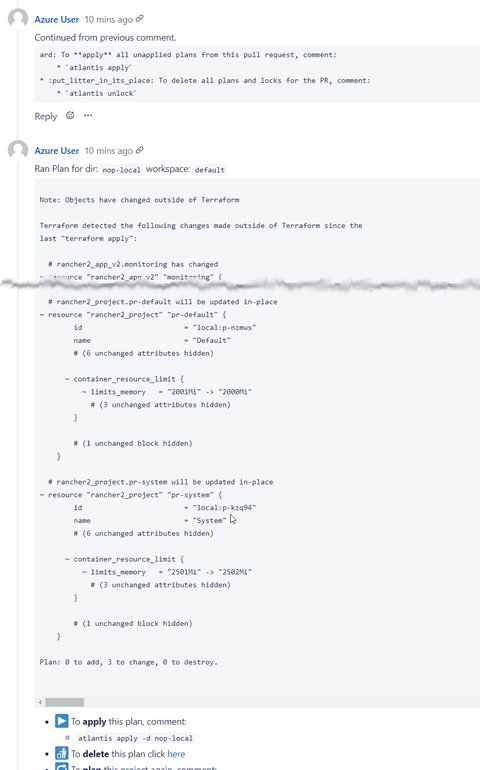
Atlantis listens for GitHub, GitLab or Bitbucket webhooks about Terraform pull requests. It then runs
terraform planand comments with the output back on the pull request.When you want to apply, comment
atlantis applyon the pull request and Atlantis will run `terraform apply`` and comment back with the output.
Even so the documentation is great, it usually is not as straight forward as it seems. So here is my situation
atlantis shall run on the on-prem kubernetes cluster
I am sitting behind a corporate proxy
we are using azure or better azure storage account to store the state of terraform
- it uses a private endpoint, but with a direct connection
code repo is an on-prem Bitbucket instance
we use self-signed certificates
Setup - the basics
I won’t go to network details, but it’s clear that you might need to open fw holes so that atlantis can talk to [Bitbucket] and Azure.
As a start, luckily, the atlantis team offers a helm-chart, which is my preferred way to install apps in the Kubernetes platform. So the installation seems pretty easy:
Create a Webhook Secret
Create a Webhook in the repo using the Secret from above
Create a Bitbucket token for user
BBUSERCreate a
values.yamlbitbucket: user: BBUSER baseURL: https://git.intra # secret: passed via cli # token: passed via cli ingress: enabled: true path: / pathType: Prefix hosts: - host: atlantis.intra paths: ["/"] tls: - secretName: wildcard-ingress-cert hosts: - atlantis.intraInstall atlantis using helm
helm repo add remote https://docker.intra/remote-helm-rancher/ helm install atlantis remote/atlantis -f values.yaml --set bitbucket.token=<TOKEN_FOR_BITBUCKET> --set bitbucket.secret=<SECRET from step 1> -n atlantis
However, the atlantis pod may not start due to the following error:
docker-entrypoint.sh: detected /atlantis-data wrong filesystem permissions
currently owned by root:atlantis, changing to atlantis:atlantis...
chown: /atlantis-data/lost+found: Operation not permitted
chown: /atlantis-data/lost+found: Operation not permitted
chown: /atlantis-data: Operation not permitted
chown: /atlantis-data: Operation not permittedThis seems to be a known issue and I just have to use an older chart (4.0.3). Unfortunately the communication to Bitbucket still did not work, cause Bitbucket uses a self-signed server certifcate, which by nature is not trusted.
Self-signed certificates
And as we are using self-signed certificates, the above setup will not work. Unfortunately it lacks of a way to inject your self-signed certificates into the trust. Sure I can build my own image which include the certs, but I prefer to rely on the offical images.
So as a first approach, I extended charts/atlantis/templates/statefulset.yaml so that one can inject additional certificates from a secret into /etc/ssl/certs
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
...
spec:
....
template:
...
spec:
...
volumes:
...
{{- if .Values.additionalTrustCerts.secretName }}
- name: additional-trust-certs
secret:
secretName: {{ .Values.additionalTrustCerts.secretName }}
{{- end }}
...
volumeMounts:
{{- if .Values.additionalTrustCerts.secretName }}
{{- range .Values.additionalTrustCerts.certs }}
- name: additional-trust-certs
mountPath: "/etc/ssl/certs/{{ . }}"
subPath: {{ . }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
...So you could add a secret .Values.additionalTrustCerts.secretName which contains root and subordinate certificates:
apiVersion: v1
data:
self-signed-root.crt: XXXXX
self-signed-subord.crt: XXXX
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-certs
namespace: atlantis
type: OpaqueAnd then as part of the values.yaml you provide the necessary .Values.additionalTrustCerts.certs
additionalTrustCerts:
secretName: my-certs
certs:
- self-signed-root.crt
- self-signed-subord.crtHowever, this does now work, as one also has to run update-ca-certificates, which ultimately will fail, as the user who is running the pod is not the root user and hence has no access to override /etc/ssl/certs/cacerts. My alternative approach is outlined in this PR. It allows you to override the /etc/ssl/certs/cacerts by your own PEM-file.
Azure cli
So once atlantis trusts my self-signed certificates, I gave it a try, but unfortunately still no success. While atlantis could now communicate with Bitbucket, but atlantis plan failed due to lack of azure-cli.
running "/usr/local/bin/terraform init -input=false -upgrade" in "/atlantis-data/repos/Kubernetes/terraform/37/default/my-kubernetes-cluster": exit status 1
╷
│ Error: Error building ARM Config: please ensure you have installed Azure CLI version 2.0.79 or newer. Error parsing json result from the Azure CLI: launching Azure CLI: exec: "az": executable file not found in $PATH.
Initializing the backend...Just copying a binary file does not work, as there is none. Unfortunatley azure-cli has a lot of dependecies to python and it’s libraries. So this is where, I had to start creating my own container. Here is the Dockerfile
FROM ghcr.io/runatlantis/atlantis:v0.19.3
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1
RUN apk add --update --no-cache python3 python3-dev musl-dev linux-headers gcc && ln -sf python3 /usr/bin/python
RUN python3 -m ensurepip
RUN pip3 install --no-cache --upgrade pip setuptools
RUN pip3 install wheel --no-cache
RUN pip install --upgrade azure-cli --no-cache-dirWe then have to use the new image in the values.yaml
image:
repository: docker.intra/papanito/atlantis-azure
tag: v0.19.3But this is not all we also have to ensure, that python knows about the self-signed certificates. So I will eventually map the certificate from above to `/usr/lib/python3.9/site-packages/certifi/cacert.pem
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: additional-trust-certs
mountPath: /usr/lib/python3.9/site-packages/certifi/cacert.pem
subPath: ca-certificates.crtAt last, we have to authenticate against azure, so the state can be read from the storage account. Following this guide we need a service principal, which has the following permissions
- Storage Blob Data Contributor - on the scope
- Storage Queue Data Contributor - on the scope of the container
If not, terraform will not be able to properly connect:
bash-5.1$ /usr/local/bin/terraform init -input=false -upgrade
Initializing the backend...
╷
│ Error: Failed to get existing workspaces: containers.Client#ListBlobs: Failure responding to request: StatusCode=403 -- Original Error: autorest/azure: Service returned an error. Status=403 Code="AuthorizationPermissionMismatch" Message="This request is not authorized to perform this operation using this permission.\nRequestId:71979092-601e-0049-1489-9abb93000000\nTime:2022-07-18T09:35:06.7502023Azure authentication
We already have azurerm configured in backend.tf:
terraform {
backend "azurerm" {
use_azuread_auth = true
tenant_id = "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
subscription_id = "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
resource_group_name = "rg-atlantis"
storage_account_name = "tfstate"
container_name = "xxxx"
key = "xxxx"
}
}In addition to that, we also need client_id and client_secret, which we can inject as environment variables ARM_CLIENT_ID and ARM_CLIENT_SECRET. I use a separate secret and add this to the values.yaml:
environmentSecrets:
- name: ARM_CLIENT_ID
secretKeyRef:
name: atlantis-azure-credentials
key: ARM_CLIENT_ID
- name: ARM_CLIENT_SECRET
secretKeyRef:
name: atlantis-azure-credentials
key: ARM_CLIENT_SECRETRancher, kubectl and webproxy
We use the following two providers:
- rancher2: Verified provider for Rancher
- kubectl: This provider is the best way of managing Kubernetes resources in Terraform, by allowing you to use the thing Kubernetes loves best - yaml!
These require a proper configuration in the backend.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
rancher2 = {
source = "rancher/rancher2"
version = "1.22.2"
}
kubernetes = {
source = "hashicorp/kubernetes"
version = "2.11.0"
}
kubectl = {
source = "gavinbunney/kubectl"
version = "1.14.0"
}
}
backend "azurerm" {
...
}
provider "rancher2" {
api_url = "${var.RANCHER_API_URL}"
access_key = "${var.RANCHER_TOKEN}"
secret_key = "${var.RANCHER__SECRET}"
}
provider "kubernetes" {
host = "${var.RANCHER_API_URL}/k8s/clusters/${rancher2_cluster.cluster.id}"
token = "${var.RANCHER_TOKEN}:${var.RANCHER_SECRET}"
}
provider "kubectl" {
load_config_file = "false"
host = "${var.RANCHER_API_URL}/k8s/clusters/${rancher2_cluster.cluster.id}"
token = "${var.RANCHER_TOKEN}:${var.RANCHER__SECRET}"
}As you can see, we use environment variables, which we also inject the same way as we did for azurerm. So let’s extend the values.yaml
environmentSecrets:
...
- name: TF_VAR_RANCHER_TOKEN
secretKeyRef:
name: rancher-credentials
key: RANCHER_TOKEN
- name: TF_VAR_RANCHER_SECRET
secretKeyRef:
name: rancher-credentials
key: RANCHER_SECRET
- name: TF_VAR_RANCHER_API_URL
secretKeyRef:
name: rancher-credentials
key: RANCHER_API_URLAt last, we also need to ensure traffic goes troug the proxy where necessary - so mainly traffic for public endpoints like the azure portal. We simply inject the proxy values as environment variables
environmentRaw:
- name: HTTP_PROXY
value: http://webproxy.intra:8888
- name: HTTPS_PROXY
value: http://webproxy.intra:8888
- name: NO_PROXY
value: localhost,127.0.0.1,.intra,tfstate.blob.core.windows.netSum up
I my environment, there are some additional steps necessary to get atlantis running. Here are all the steps to be performed:
Create a Webhook Secret
Create a Webhook in the repo using the Secret from above
Create a Bitbucket token for user
BBUSERAdd secret
my-ca-certificateswhich self-signed root and subordinates certificates in single pem file calledca-certificates.crtCreate a service prinicipal in azure in azure, which has access to the storage account where the tf state is stored. It shall have the following permissions
In Rancher, create a serivce user (admin) and a token for it
Add secret
rancher-credentialswith credentials for each Rancher instancekubectl create secret generic rancher-credentials -n atlantis --context nop \ --from-literal=TF_VAR_PLAYGROUND_TOKEN=<TOKEN> --from-literal=TF_VAR_RANCHER_SECRET=<SECRET> --from-literal=TF_VAR_RANCHER_API_URL=https://rancher.intraAdd secret
atlantis-azure-credentialswith credentials for azure service principalkubectl create secret generic atlantis-azure-credentials -n atlantis --context nop --from-literal=ARM_CLIENT_ID=<CLIENT_ID> --from-literal=ARM_CLIENT_SECRET=<CLIENT_SECRET>Create a
values.yaml# this specific image contains az plus dependencies image: repository: docker.intra/papanito/atlantis-azure tag: v0.19.3 bitbucket: user: BBUSER baseURL: https://git.intra # secret: passed via cli # token: passed via cli ingress: enabled: true path: / pathType: Prefix hosts: - host: atlantis.intra paths: ["/"] tls: - secretName: wildcard-ingress-cert hosts: - atlantis.intra orgAllowlist: git.intra/tf/rancher customPem: my-ca-certificates environmentRaw: - name: HTTP_PROXY value: http://webproxy.intra:8888 - name: HTTPS_PROXY value: http://webproxy.intra:8888 - name: NO_PROXY value: localhost,127.0.0.1,.intra,tfstate.blob.core.windows.net environmentSecrets: - name: ARM_CLIENT_ID secretKeyRef: name: atlantis-azure-credentials key: ARM_CLIENT_ID - name: ARM_CLIENT_SECRET secretKeyRef: name: atlantis-azure-credentials key: ARM_CLIENT_SECRET - name: TF_VAR_RANCHER_TOKEN secretKeyRef: name: rancher-credentials key: RANCHER_TOKEN - name: TF_VAR_RANCHER_SECRET secretKeyRef: name: rancher-credentials key: RANCHER_SECRET - name: TF_VAR_RANCHER_API_URL secretKeyRef: name: rancher-credentials key: RANCHER_API_URLInstall atlantis using helm
Remarks: Currently I am are using a modified chart until PR #163 is merged.
helm repo add remote https://docker.intra/remote-helm-rancher/
helm install atlantis remote/atlantis -f values.yaml --set bitbucket.token=<TOKEN_FOR_BITBUCKET> --set bitbucket.secret=<SECRET from step 1> -n atlantisSo now, atlantis runs a terraform plan upon a pull request