What is Stackrox (Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes)?
Posted on May 17, 2021 by Adrian Wyssmann ‐ 5 min read
At my current employer we use a container security platform called Stackrox, which recently was acquired by RedHat. But that is it exactly and for what is it good?
What is Stackrox/RHACS?
StackRox is a full-lifecycle Kubernetes security solution, which allows you do detect, manage and mitigate security risks (e.g. wrong configuration), as well as vulnerabilities (CVEs). It offers you not only a comprehensive view of security policy violations but also enables you to create and modify policies, that help you to minimize risks based on configurations, vulnerabilities, and other factors and help you to implement security and DevOps best practices. It also integrates with other tools including your CI system.
This Youtube Video gives a very nice introduction on what it does, and how it works.
RHACS
Since RedHat acquired Stackrox, they also start re-branding the tool zo Red Hat® Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes (RHACS)
The best thing of that is that since version 3.0.58.0 all licensing restrictions have been removed. There are some plans to have an OSS version, plus and Enterprise version
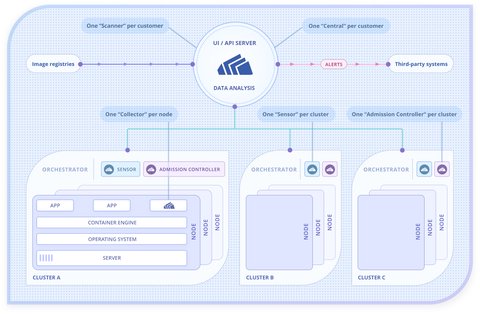
Architecture
Stackrox contains of several components:
| Component | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Central | Main component, gathers and displays information from other components.Handles data persistence, API interactions and UI access. | 1 for multiple clusters. |
| Sensor | Monitors the cluster: Collects and augments data from the Collector. | 1 for each cluster. |
| Scanner | Scans images for vulnerabilities. It analyzes all image layers to check for known vulnerabilities from the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) list. Scanner also identifies vulnerabilities that are installed by package managers and language-level dependencies. | 1 for multiple clusters. |
| Collector | Collects and monitors container activities (container runtime and network activity) | 1 on each node. |
| Admission controller (optional) | Interacts with Kubernetes API server and prevents creating workloads that don’t adhere to security policies. | 1 for each cluster. |
What can you do with Stackrox?
Well there are a bunch of stuff. A nice dashboard is the entry point
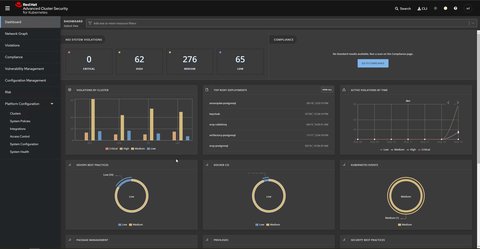
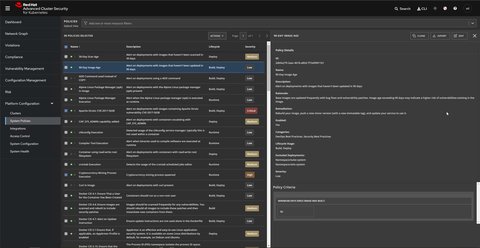
Manage security policies
You can define security policies - or use pre-defined ones - to prevent high-risk service deployments. A policy checks for certain aspects e.g. container does not run in privileged mode or check for container not updated for 30+ days. Each policy has a Severity - Critical, High, Medium or Low - and is applied to one or more of the following stages:
- Build - Fails your continuous integration (CI) builds when images match the conditions of the policy.
- Deploy - Blocks creation of deployments that match the conditions of the policy. In clusters with admission controller enforcement, the Kubernetes (or OpenShift) API server blocks all noncompliant deployments. In other clusters, the StackRox Kubernetes Security Platform edits noncompliant deployments to prevent pods from being scheduled.
- Runtime - Kills all pods that match the conditions of the policy.
There are a lot of policy criteria which can be configured. By default policy violations are reported, but not enforced. One however enabling the admission controller enforcement by turing on the Admission Controller Webhook, which then ensures the policies are met or otherwise blocks deployments or kills pods.
Breakglass
The admission controller enforcement can be by-passed, by adding
admission.stackrox.io/break-glassannotation to your configuration YAML.
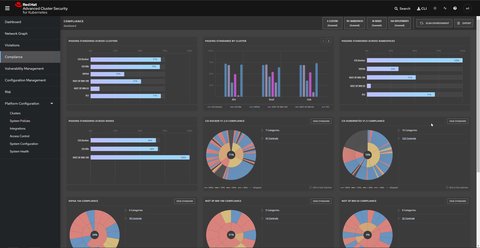
Manage compliance
Stackrox allows automated check and validation of compliance for the different industry standards:
- CIS Benchmarks (Center for Internet Security) for Docker and Kubernetes,
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act),
- NIST Special Publication 800-190 and 800-53 (National Institute of Standards and Technology), and
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
The scanning allows you to evaluate and harden your infrastructure (Docker Engine, Kubernetes orchestrator) to be compliant with these standards.
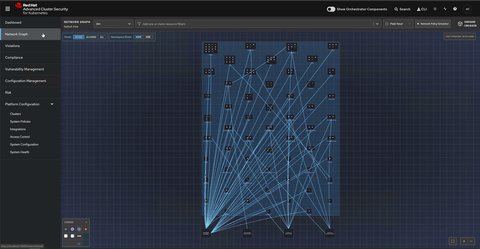
Manage network policies
This feature allows you to visualize existing network policies, simulate proposed policies, and generate new policies based on actual traffic.
A Kubernetes network policy is a specification of how groups of pods are allowed to communicate with each other and other network endpoints. These network policies are configured as YAML files.
- Network graph: Visualize allowed network connections and active communication paths among namespaces and deployments
- Network policy simulator: upload new network policy configuration files, and preview the network policies visually
- Network policy generator: Generate a network policy configuration file (YAML) based on the network communication flows in your environment within a specified period
Vulnerability management
Stackrox detect vulnerabilities (CVEs) and them mitigation by enforcing actions defined in the [policies]((#manage-security-policies) Also can Stackrox analyze docker images for vulnerabilities, where all image layers are analyzed for known vulnerabilities (CVEs)
StackRox Central submits image scanning requests to StackRox Scanner. Upon receiving these requests, StackRox Scanner pulls image layers from the relevant registry, checks the images, and identifies installed packages in each layer. Then it compares the identified packages and programming language-specific dependencies with vulnerability lists and sends information back to StackRox Central.
How to install?
Helm charts for the StackRox Kubernetes Security Platform offers helm-charts for installing stackrox. Since version 3.0.50.0 there is also a central-services chart, which was not available before. The official documentation offers a detailed how-to on the installation process.
Ensure that the remote docker repo for stackrox.io is setup. Alternatively registry.redhat.io could be used but it requires authentication
Install central-services
Installation Instructions can be found here
Install helm chart
helm install stackrox-central-services remote/stackrox-central-services --values values.yml -n stackroxYou can test the central dashboard by forwarding the port 18443
kubectl -n stackrox port-forward svc/central 18443:443Create ingress to central
Install Sensors
After we installed central, we have to install the sensors in each cluster following this guideline
Register (create) a cluster in Stackrox central
You should provide configurations according to your environment e.g. providing a custom registry for sensor and collector images
On the StackRox portal, navigate to
Platform Configuration>Clusters.Select
+.Specify configuration: Replace your endpoints and docker repos according to your setup

Click
Nextto apply the sensor configuration.Click
Download Yaml File and Keysto continue with sensor setup. This creates a zip file.
Unzip zip file to
./sensors/e.g../sensors/sensor-devEnsure you work in the correct cluster and run
sensor.shwhich can be found under the recently extracted foldercluster=dev export KUBE_COMMAND="kubectl --context $cluster" && \ ./sensors/sensor-$env/sensor.shRemarks
Running the
sensor.shunder Windows failed while the script tried to create the registry credentials:$ ./sensor.sh Using authentication token for docker.intra from ~/.docker/config.json. error: error parsing STDIN: error converting YAML to JSON: yaml: line 5: could not find expected ':'I actually fixed that by creating the necessary
docker-registrysecretsstackroxandcollector-stackroxmanually:kubectl --context $cluster -n stackrox create secret docker-registry stackrox ` --docker-server=$registry_url ` --docker-username=$username ` --docker-password=$password ` --docker-email="[email protected]"